Solanum boliviense

| Common Names | Hampatu papa, Qquita papa, Papa aromatica |
| Code | blv |
| Synonyms | S. alticola, S. astleyi, S. megistacrolobum, S. sanctae-rosae, S. toralapanum, S. ureyi |
| Clade | 4 |
| Series | Megistacroloba |
| Ploidy | Diploid (2x) |
| EBN | 2 |
| Tuberization Photoperiod | Short Day |
| Self-compatibility | No |
| Nuclear Genome | A |
| Cytoplasmic Genome | W |
| Citation | Dunal: A. L. P. P. de Candolle, Prodr. 13(1):43. 1852 |
Description
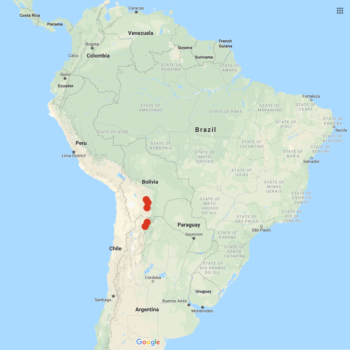
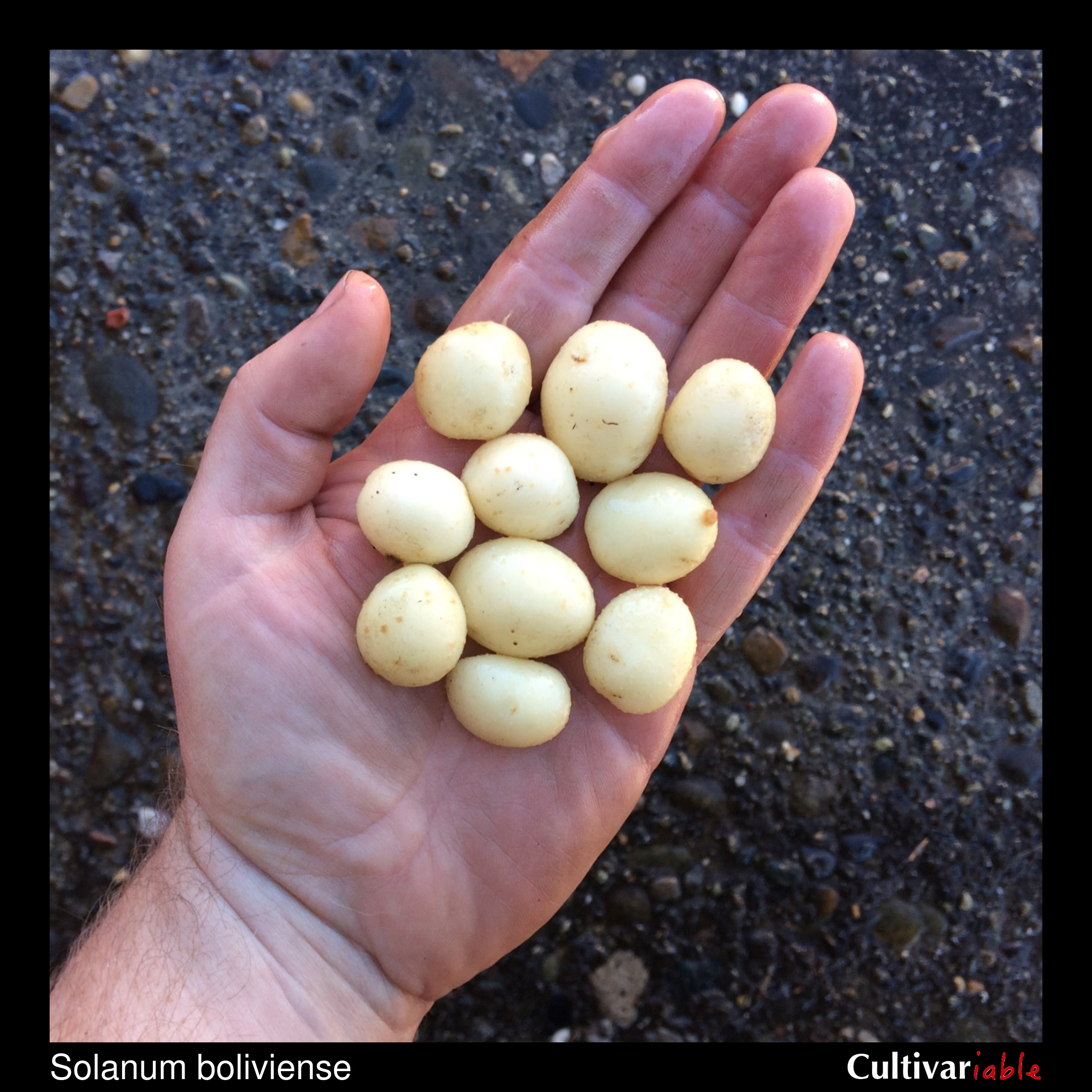
Solanum boliviense is primarily a Bolivian species, but is found from southern Peru to northern Argentina. A plant of poor soils, growing up to about the 13,750 foot elevation, where frosts occur fairly frequently. Plants variable in form, from low growing rosettes to erect plants reaching about 15 inches in height. Stolons two feet long or more. Tubers small and round, reaching about an inch in diameter, and sometimes moniliform (forming chains). Flowers blue to purple.
The specific epithet, boliviense, refers to the region of maximum diversity for this species: Bolivia. While there is no completely standardized pronunciation for scientific names, the most common way to pronounce this species is probably so-LAY-num boh-lih-vee-EN-say.
Subramanian (2017) found that at least some accessions of this species have unusually high potassium content and unusually low dry matter (as S. megistacrolobum).
This species has been tentatively classified as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List (Cadima 2014).
Resistances
This species carries a Potato Virus M resistance gene, Rm, on chromosome 11.
This species can survive frosts down to 22 degrees F (-5.5 C) (Li 1977, as S. sanctae-rosae). Vega (1995) found that this species is more frost tolerant than domesticated potato.
| Condition | Type | Level of Resistance | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria solani (Early Blight) | Fungus | Somewhat resistant | Jansky 2008(as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Drought | Abiotic | Somewhat resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Frost | Abiotic | Resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Fusarium sambucinum (Fusarium Wilt) | Fungus | Resistant | Lynch 2003 (including S. sanctae-rosae) |
| Globodera pallida (Pale Cyst Nematode) | Invertebrate | Somewhat resistant | Castelli 2003 |
| Globodera pallida (Pale Cyst Nematode) | Invertebrate | Not resistant | Bachmann-Pfabe 2019 |
| Globodera rostochiensis (Potato Cyst/Golden Nematode) | Invertebrate | Somewhat resistant | Castelli 2003 |
| Heat | Abiotic | Somewhat resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Colorado Potato Beetle) | Invertebrate | Somewhat resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Meloidogyne spp. (Root Knot Nematode) | Invertebrate | Somewhat resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 |
| Myzus persicae (Green Peach Aphid) | Invertebrate | Somewhat resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Pectobacterium carotovorum (Blackleg/Soft Rot) | Bacterium | Somewhat resistant | Chung 2011, Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Phytophthora infestans (Late Blight) | Fungus | Somewhat resistant | Gonzales 2002 |
| Phytophthora infestans (Late Blight) | Fungus | Resistant | Bachmann-Pfabe 2019 |
| Potato Leaf Roll Virus (PLRV) | Virus | Somewhat resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Potato Virus M (PVM) | Virus | Somewhat resistant | Marczewski 2006 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Potato Virus S (PVS) | Virus | Somewhat resistant | Santillan 2018 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Potato Virus X (PVX) | Virus | Resistant | Horvath 1989 (as S. astleyi) |
| Potato Virus Y (PVY) | Virus | Not resistant | Cai 2011 |
| Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (White Mold) | Fungus | Not resistant | Jansky 2006 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
| Synchytrium endobioticum (Wart) | Fungus | Somewhat resistant | Machida-Hirano 2015 (as S. megistacrolobum) |
Glykoalkaloid content
Johns (1986b) found glycoalkaloid levels ranging from 1.2 to 26 mg /100 g for S. boliviense (including S. sanctae-rosae). The primary glycoalkaloids was tomatine, but demmisine and commersonine were also present in some accessions.
Images
Cultivation
I have found seeds of this species easy to germinate using the standard conditions for S. tuberosum, although sometimes slow.
Towill (1983) found that seeds of this species stored at 1 to 3 degrees C germinated at 78 to 100% after 18 years (including S. megistacrolobum).
Bamberg (2018) found that alternating temperatures increased germination in this species.
Bamberg (1995) found that at least some accessions of S. boliviense are able to produce a significant amount of viable pollen even when temperatures exceed 100 degrees F for several hours during the day. Flowering was reduced under these conditions.
Bamberg (2017) found a 110% increase in seed set in this species with supplemental applications of liquid fertilizer at four and seven weeks after potting.
Trapero-Mozos (2018) determined that this species will tolerate a temperature of 40 C after acclimation for a period of time at 25 C.
Breeding
Crosses with S. tuberosum
S. boliviense was used in the breeding of the variety ‘Conestoga’ (Plaisted 1989).
| Female | Male | Berry Set |
Seed Set | Germ | Ploidy | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. boliviense (including S. astleyi, S. megistacrolobum, S. sanctae-rosae, and S. toralapanum) | S. tuberosum 4x | None | None | Jackson (1999) | ||
| S. tuberosum 2x | S. boliviense | Low | Low | Diploid | S. ajanhuiri | |
| S. tuberosum 4x | S. boliviense (including S. astleyi, S. megistacrolobum, S. sanctae-rosae, and S. toralapanum) | Minimal | Minimal | Jackson (1999) |
Crosses with other species
Jackson (1999) found 4-16% 2n pollen for varieties of this species. Ochoa (1990) reported 5% 2n pollen for two accessions.
| Female | Male | Berry Set |
Seed Set | Germ | Ploidy | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. boliviense | S. acaule | High | Moderate | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. boliviense | S. berthaultii (as S. tarijense) | High | High | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. boliviense | S. brevicaule (as S. alandiae, S. vidaurrei) | High | High | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. boliviense | S. candolleanum (as S. abancayense) | High | High | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. boliviense | S. candolleanum (as S. bukasovii) | Low | Low | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. boliviense | S. infundibuliforme | High | High | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. brevicaule | S. boliviense | High | High | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. candolleanum | S. boliviense | High | High | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. candolleanum (as S. coelestipetalum) | S. boliviense | None | None | Ochoa (1990) | ||
| S. candolleanum (as S. sparsipilum) | S. boliviense | Low | Low | Ochoa (1990) |
References
Solanum boliviense at Solanaceae Source














