Solanum verrucosum

| Common Names | Papa morda |
| Code | ver |
| Synonyms | S. macropilosum |
| Clade | 4 |
| Series | Tuberosa |
| Ploidy | Diploid (2x), Triploid (3x), Tetraploid (4x) |
| EBN | 2 |
| Tuberization Photoperiod | Unknown |
| Self-compatibility | Yes |
| Nuclear Genome | A |
| Cytoplasmic Genome | W, D |
| Citation | Von Schlechtendal: Index Seminum Hort. Halensis: 10. 1839. |
Description
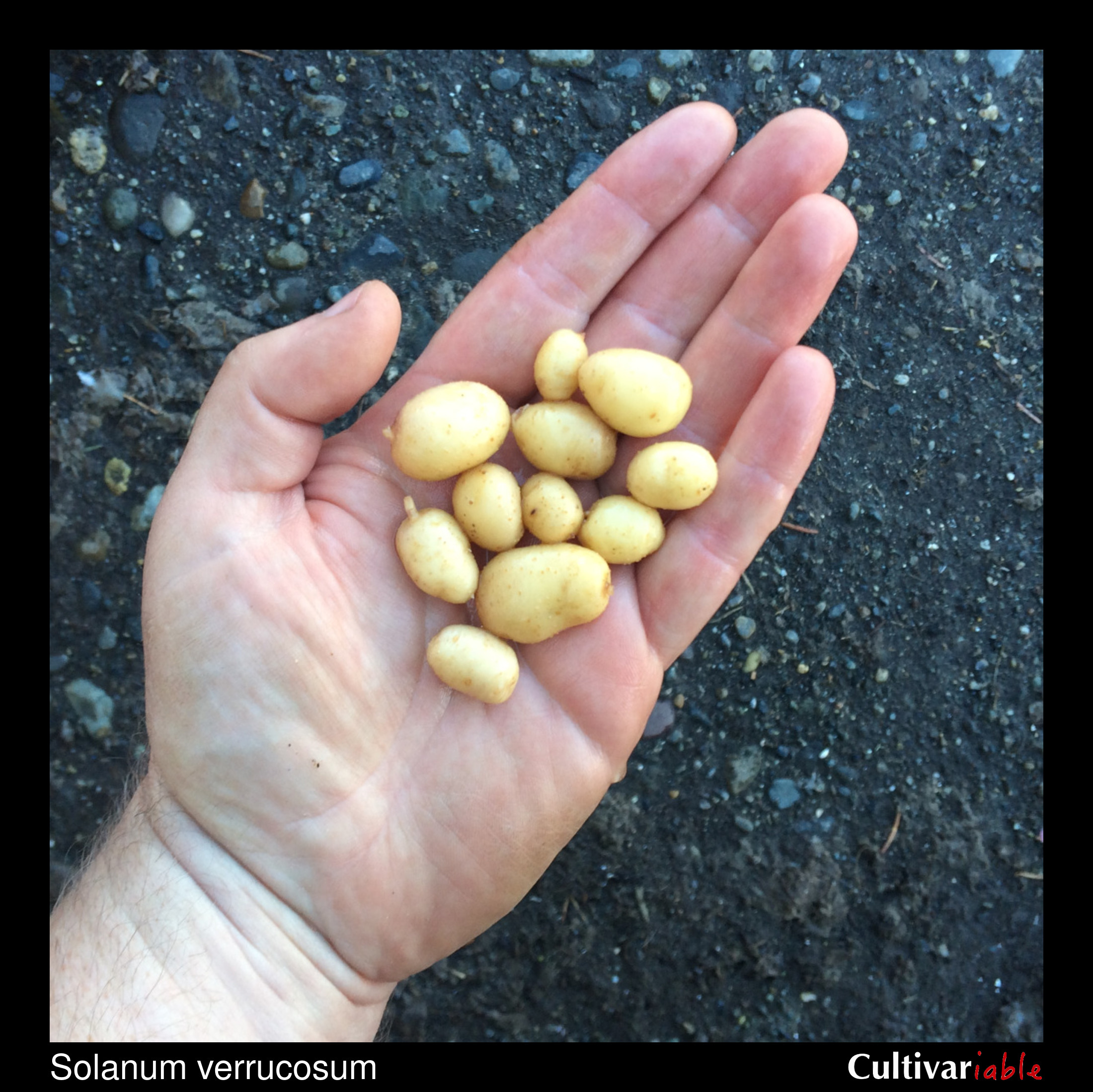
Solanum verrucosum is a widespread species in Mexico, where it is primarily a plant of woodlands and cloud forests. Plants about 6 to 18 inches tall. Blue flowers. Round berries.
The specific epithet, verrucosum, means “warty,” but I’m not sure what the context is. While there is no completely standardized pronunciation for scientific names, the most common way to pronounce this species is probably so-LAY-num ve-ROO-koh-sum.
Tubers of this species are or were occasionally eaten in Mexico, according to notes from various collecting expeditions. Correll (1962) also reports that this species was once cultivated near Geneva, Switzerland, in the hope that it would resist late blight, but eventually abandoned due to the small tuber size and late bearing.
This species is remarkable for its self-compatibility, although inbred lines do suffer from inbreeding depression as expected in diploids of this genus (Abdalla 1973). Self compatibility is rare in diploid potatoes and has only been otherwise observed in S. polyadenium and certain lines of S. chacoense that possess self-incompatibility inhibition (sli) alleles.
S. verrucosum is suspected as the progenitor of all Mexican polyploid species, based upon the presence of a mitochondrial marker (Sanetomo 2013). It is the only North American diploid species with the A genome.
Resistances
This species can survive frosts down to 27 degrees F (-3 C) (Li 1977). Vega (1995) found that this species is about as frost tolerant as domesticated potato.
Some accessions of this species carry the RB gene, conferring late blight resistance.
| Condition | Type | Level of Resistance | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria solani (Early Blight) | Fungus | Somewhat resistant | Jansky 2008 |
| Globodera pallida (Pale Cyst Nematode) | Invertebrate | Not resistant | Bachmann-Pfabe 2019 |
| Globodera pallida (Pale Cyst Nematode) | Invertebrate | Not resistant | Castelli 2003 |
| Globodera rostochiensis (Potato Cyst/Golden Nematode) | Invertebrate | Not resistant | Castelli 2003 |
| Pectobacterium carotovorum (Blackleg/Soft Rot) | Bacteria | Somewhat resistant | Chung 2011 |
| Phytophthora infestans (Late Blight) | Fungus | Somewhat resistant | |
| Phytophthora infestans (Late Blight) | Fungus | Somewhat resistant | Bachmann-Pfabe 2019 |
| Phytophthora infestans (Late Blight) | Fungus | Some resistance | Karki 2020 |
| Potato Virus Y (PVY) | Virus | Not resistant | Cai 2011 |
Glykoalkaloid content
Images
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
Cultivation
Towill (1983) found that seeds of this species stored at 1 to 3 degrees C germinated at 100% after 27 years.
Breeding
Crosses with S. tuberosum
Watanabe (1991) found that 4.1% of varieties of this species produced 2n pollen, which would be effectively tetraploid and 4EBN.
| Female | Male | Berry Set |
Seed Set | Ploidy | Germ | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. tuberosum | S. verrucosum | Minimal | None | Jackson (1999) | ||
| S. verrucosum | S. tuberosum | None | None | Jackson (1999) | ||
| S. verrucosum | S. tuberosum 2x | Moderate | Moderate | High | Abdalla 1973 |
Crosses with other species
Jackson (1999) found 4-11% 2n pollen for varieties of this species.
Abdalla (1973) observed that interspecies crosses in which S. verrucosum is used as the male parent are rarely successful. In addition, cytoplasmic sterility renders the majority of the progeny male sterile when S. verrucosum is used as the female parent.
| Female | Male | Berry Set |
Seed Set | Ploidy | Germ | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. commersonii | S. verrucosum | Yes | Yes | Yes | 2x | Propach 1940 |
| S. verrucosum | S. chacoense | High | High | Low | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. chomatophilum | Low | Moderate | High | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. infundibuliforme | High | High | Moderate | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. raphanifolium | High | Low | High | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. berthaultii (as S. tarijense) | High | Moderate | Minimal | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. candolleanum (as S. canasense and S. multidissectum) | High/Moderate | Low/Moderate | Low/Moderate | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. kurtzianum | High | High | High | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. brevicaule (as S. leptophyes) | High | Low | Low | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. microdontum (as S. gigantophyllum) | Moderate | Moderate | High | Abdalla 1973 | |
| S. verrucosum | S. vernei | High | Moderate | High | Abdalla 1973 |
